One of the transformative technologies that is reshaping the telecom industry is certainly Artificial Intelligence. AI is playing a pivotal role in Customer Value Management (CVM) for CSPs, revolutionizing how they understand, engage with, and retain their customers. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the multifaceted ways AI is making a significant impact on CVM strategies, ultimately enhancing the overall customer experience.
In 2024, the role of AI in Customer Value Management solution for Communication Service Providers (CSPs) is essential. These advanced AI-driven systems offer crucial insights into customer behavior and preferences, empowering CSPs to deliver tailored services and experiences. CVM AI enables predictive modeling for personalized offerings, ensuring enhanced customer satisfaction and reduced churn rates.
The global artificial intelligence in telecommunication market size is projected to be valued at $1,180.9 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach $14,496 million by 2033, with a notable CAGR of 28.5% from 2023 to 2033. Additionally, in a competitive market, these tools play a pivotal role in identifying new revenue streams and optimizing operational efficiency, ultimately cementing CSPs’ positions as innovative market leaders in the telecom industry.
AI-powered CVM solutions have become indispensable tools, revolutionizing how CSPs understand, engage with, and cater to their diverse customer base. Leveraging advanced algorithms, AI in CVM helps predict customer behavior, anticipate preferences, and recommend tailored services, fostering personalized interactions that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty. Moreover, these technologies empower CSPs to optimize marketing strategies, efficiently manage resources, and dynamically adapt to market trends, ensuring a competitive edge in an ever-evolving industry. With AI-infused CVM, CSPs are poised to unlock unparalleled insights, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and strategically navigate the evolving telecom landscape in 2024 and beyond.
The Impact of AI in Telco to Redefine CSPs
In the ever-evolving landscape of Communication Service Providers, Artificial Intelligence applications stand at the forefront, reshaping customer engagement strategies.
1. Predictive Analytics for Customer Behavior:
One of the standout features of AI in CVM is its ability to leverage predictive analytics. Telecom operators can harness the power of AI algorithms to analyze vast amounts of customer data, identifying patterns and predicting future behaviors. By understanding customer preferences, usage patterns, and potential churn indicators, operators can proactively tailor their offerings and engagement strategies. For instance, AI can predict when a customer might be considering a switch to another provider based on historical data, allowing operators to intervene with targeted retention offers.
2. Personalized Offers and Recommendations:
AI’s capacity to process and analyze vast datasets enables telecom operators to create highly personalized offers and recommendations for their customers. By considering factors such as usage history, preferences, and even real-time interactions, AI algorithms can generate targeted promotions that are more likely to resonate with individual customers. This not only enhances the customer experience but also increases the likelihood of upselling additional services or retaining customers through tailored incentives.
3. Intelligent Customer Service:
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service in the telecom industry. These intelligent systems can handle routine inquiries, troubleshoot common issues, and provide real-time support. By incorporating natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, AI-powered customer service becomes increasingly adept at understanding and addressing customer queries, ultimately reducing response times and improving overall customer satisfaction.
4. Churn Prediction and Prevention:
Churn is a critical concern for telecom operators, and AI is proving to be a valuable asset in predicting and preventing customer churn. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns that precede customer attrition, AI algorithms can provide early warnings, allowing operators to take proactive measures. Whether it’s offering personalized discounts, introducing loyalty programs, or addressing specific pain points, AI enables telecom operators to implement targeted strategies to retain at-risk customers.
5. Customer Segmentation and Targeted Marketing:
AI facilitates sophisticated customer segmentation by categorizing users based on their behaviors, preferences, and demographics. This enables telecom operators to create highly targeted marketing campaigns tailored to specific customer segments. Whether promoting new services, announcing promotions, or encouraging engagement, AI-driven segmentation ensures that marketing efforts are precise and relevant, maximizing their impact.
6. Enhanced User Experience through Natural Language Processing:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subset of AI that empowers machines to understand and interpret human language. In the context of telecom operations, NLP can be integrated into customer interfaces, allowing users to interact with devices and services using natural language. This enhances the user experience by making interactions more intuitive and user-friendly.
In the realm of Telecom Customer Value Management (CVM), various AI algorithms are leveraged to extract valuable insights and optimize customer experiences. Machine Learning (ML) algorithms like regression analysis, clustering, and decision trees play pivotal roles in predictive analytics, aiding in customer segmentation, churn prediction, and personalized offerings.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) facilitates sentiment analysis, enabling CSPs to comprehend and respond to customer sentiments across various communication channels. Deep learning models such as neural networks enhance pattern recognition, aiding in fraud detection and network optimization. These AI-driven algorithms collectively empower telecom operators to delve deeper into customer behaviors, forecast trends, and refine their services for an unparalleled user experience.
AI Models for Customer Value Management
Below are several types of AI algorithms commonly employed in CVM for telecom operators:
The implementation of Artificial Intelligence in Customer Value Management for telecom operators involves the utilization of various algorithms, each tailored to perform specific tasks efficiently. Machine Learning (ML) algorithms such as Decision Trees are instrumental in classifying customers based on their behavior and preferences, enabling the prediction of their future actions.
Clustering algorithms like K-Means facilitate the segmentation of customers into distinct groups, allowing personalized targeting for marketing campaigns. These algorithms collectively empower telecom operators to anticipate customer needs, personalize engagements, and make data-driven decisions for superior service delivery and customer satisfaction.
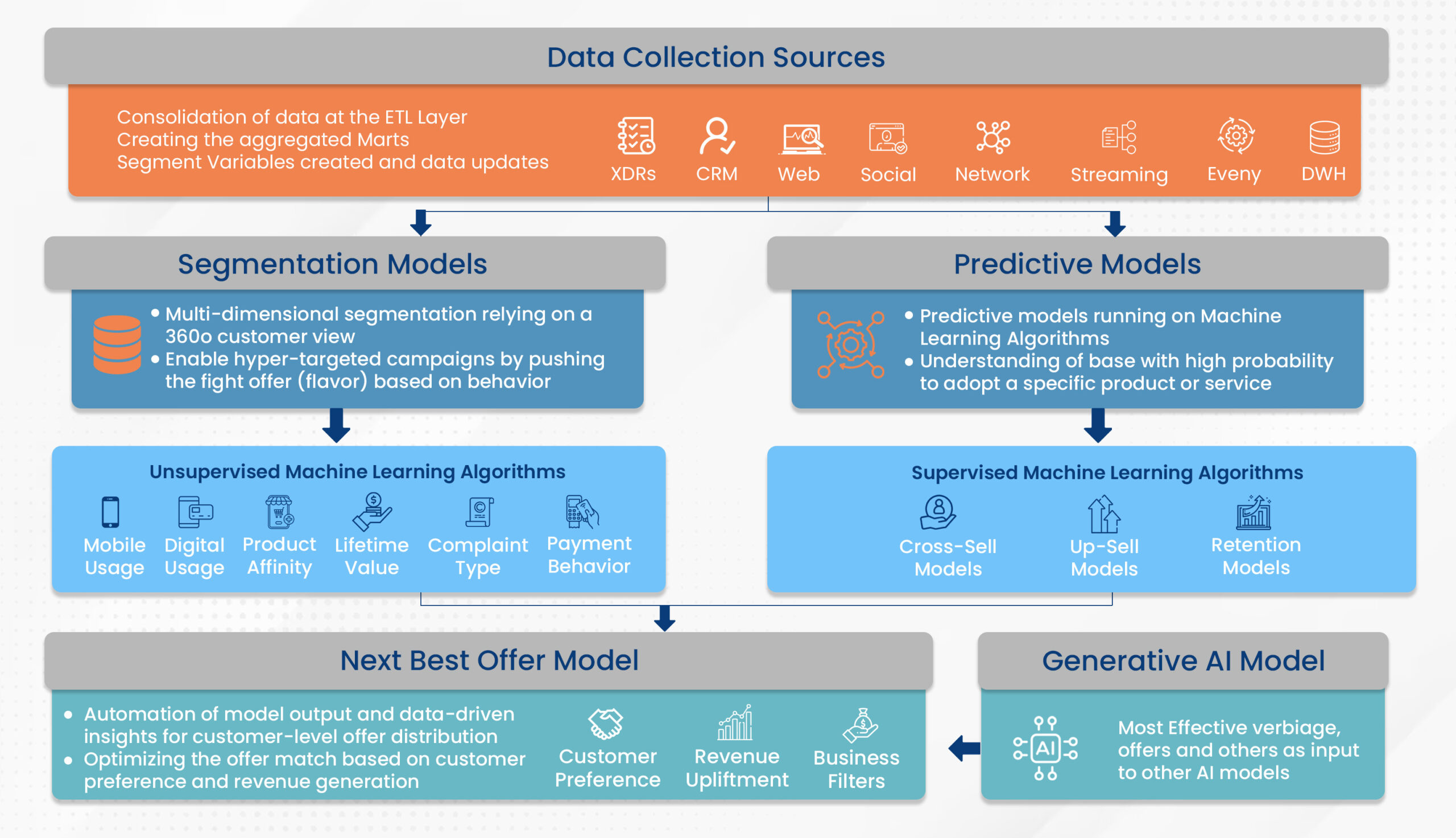
1. Predictive Analytics Algorithms:
Linear Regression:
Predicts a numerical outcome based on historical data, such as forecasting future customer spending patterns or predicting the likelihood of churn.
Use Case: Linear Regression provides a straightforward approach to estimating the relationship between various customer attributes and their potential value, aiding telecom operators in making data-driven decisions for customer engagement and resource allocation. By understanding the factors that contribute to customer value, operators can proactively implement strategies to retain high-value customers, identify up-selling opportunities, and optimize resource allocation.
Logistic Regression:
Suitable for binary outcomes, often used in predicting customer churn or the success of targeted marketing campaigns.
Use Case: Logistic Regression provides a binary classification model that is well-suited for predicting whether a customer is likely to churn or not based on relevant features. Telecom operators can implement retention strategies for at-risk customers, ultimately maximizing customer lifetime value and reducing revenue loss
2. Machine Learning Algorithms:
Decision Trees:
Useful for segmenting customer data into groups, identifying patterns, and making decisions based on specific criteria.
Use Case: The primary objective of applying Decision Trees in this use case is to build a model that segments telecom customers into distinct groups based on their characteristics. Decision Trees can effectively segment customers based on various features and behaviors, enabling telecom operators to tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
Random Forest:
An ensemble of decision trees that provides more robust and accurate predictions by aggregating multiple models.
Use Case: Churn prediction is crucial for telecom operators as it allows them to proactively identify and address customers at risk of leaving. Random Forest, by combining multiple decision trees, offers a robust and accurate model for predicting churn based on various customer attributes and behaviors.
Gradient Boosting:
Boosts the performance of weak predictive models, enhancing accuracy in tasks like predicting customer behavior.
Use Case: The goal is to build a predictive model that estimates the future value that each customer is likely to bring to the business. Gradient Boosting, by combining the predictions of multiple weak learners, provides a powerful tool for accurately forecasting customer value based on various attributes and behaviors.
3. Clustering Algorithms:
K-Means
It segments customers into clusters based on similar characteristics, aiding in personalized marketing and service strategies.
Use Case: The CVM goal is to group telecom customers into distinct segments based on shared characteristics and behaviors. By doing so, telecom operators can tailor their services, marketing strategies, and customer engagement efforts to better meet the specific needs of each segment. This segmentation enables operators to understand different customer profiles and implement personalized services, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and maximizing the overall customer lifetime value.
Hierarchical Clustering
It forms a hierarchy of clusters, revealing relationships between different customer segments.
Use Case: Hierarchical Clustering can play a crucial role in segmenting telecom customers into distinct groups based on their behaviors, preferences, and usage patterns, allowing operators to tailor their strategies for improved customer satisfaction and business outcomes.
4. Recommender System Algorithms:
Collaborative Filtering
It recommends products or services based on the preferences and behaviors of similar customers.
Use case: The primary objective is to leverage the preferences and behaviors of similar customers to make targeted service recommendations. This approach enhances customer satisfaction, increases engagement, and ultimately maximizes the overall customer lifetime value. By analyzing the behavior and preferences of similar users, operators can suggest relevant services, plans, or features to enhance the customer experience and optimize their value to the business.
Content-Based Filtering
It suggests items based on the attributes and features of products or services preferred by a particular customer.
Use case: The primary goal of applying Content-Based Filtering in this use case is to offer personalized service recommendations to telecom customers. By understanding individual preferences and usage patterns, operators can suggest relevant services, plans, or features that cater to the specific needs of each customer, thereby maximizing their value to the business.
5. Deep Learning Algorithms:
Neural Networks:
Mimic the human brain’s structure to analyze complex patterns in large datasets, useful for tasks like image recognition or predicting customer behavior.
Use case: The objective is to build a sophisticated model that predicts the future value that each customer is likely to bring to the business. Neural Networks, with their ability to capture complex relationships in data, offer a robust approach to estimating customer value based on various attributes and behaviors.
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM):
A type of recurrent neural network (RNN) suitable for sequential data, such as analyzing patterns in customer interactions over time.
Use case: The objective is to leverage the sequential nature of customer interactions to build a model that can effectively capture and learn from temporal patterns, providing accurate predictions of churn behavior. By considering the sequential dependencies in customer data, operators can proactively identify customers at risk of churn and implement targeted retention strategies.
6. Anomaly Detection Algorithms:
Isolation Forests:
It identifies anomalies or outliers in customer behavior, helping operators detect potential fraud or unusual patterns that may indicate service issues.
Use Case: The objective is to identify unusual patterns or behaviors in customer interactions that may indicate fraudulent activities. By leveraging Isolation Forests, operators can proactively detect and mitigate fraud, thereby protecting the integrity of their services and ensuring the security of customer accounts. This approach enhances security, reduces financial losses, and safeguards the overall customer experience.
7. Association Rule Learning Algorithms:
Apriori Algorithm:
It discovers associations between different products or services that are frequently purchased together, informing bundling or cross-selling strategies.
Use case: The objective is to discover patterns of co-occurrence among different telecom services, helping operators understand which services are often used together. This insight can be leveraged to optimize service bundling, enhance customer experience, and increase overall customer value. By identifying frequently co-occurring services, operators can offer targeted bundles that align with customer preferences, increasing the overall value derived from service subscriptions.
8. Genetic Algorithms:
Optimization:
It is used to optimize complex problems, such as finding the most effective combination of parameters for targeted marketing campaigns or resource allocation.
Use case: The objective is to use genetic algorithms to evolve and refine decision-making processes, leading to more effective resource allocation, personalized offerings, and ultimately, increased customer value.
9. Time Series Analysis Algorithms:
ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average):
It analyzes time-series data, beneficial for predicting trends in customer behavior over time.
Use case: The objective is to leverage time-series analysis to predict future spending behavior, enabling telecom operators to anticipate revenue trends, allocate resources effectively, and optimize customer engagement strategies. Helps to to build a predictive model that forecasts future customer spending based on historical data.
Transforming Telecom With The Evolutionary Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Customer Value Management
In the dynamic landscape of telecommunications, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a pivotal force. 6D Technologies’ Magik, an AI-powered CVM platform, stands at the forefront of this evolution to explore the impact of AI in telcos. Leveraging AI algorithms, Magik empowers telecom operators to predict customer behavior, enhance engagement, and optimize services. Through AI-driven insights, telcos gain the ability to navigate market trends, anticipate customer needs, and foster sustainable growth. The journey of AI in telecom is just beginning, and with Magik, the industry is poised to evolve and thrive in the era of intelligent connectivity.
Thought Leadership Insights: Manoj Jain, Global Head Marketing




